

The body needs to reach the stage of deep sleep, and this is confirmed by the fact that people who are deprived of sleep experience a “rebound” effect and find themselves having more slow wave sleep than normal as the body tried to compensate for the deep sleep it missed.

Since it’s also been shown to improve bone density, exercise capacity, and longevity, slow wave sleep is compelling proof that a lot of 20 minute naps is no substitute for a long, restful sleep-75 percent of the body’s production of growth hormone takes place during slow wave sleep.
DEEP SLEEP STAGE PATCH
One of the reasons this cortisol suppression is significant is its relationship to what is sometimes considered the hormone’s antidote: Growth hormone. A powerful cocktail that promotes fat loss and muscle gain, the surge in GH during deep sleep allows the body to patch the wear and tear of the day by helping to repair micro tears in muscles and make them stronger than they were before.
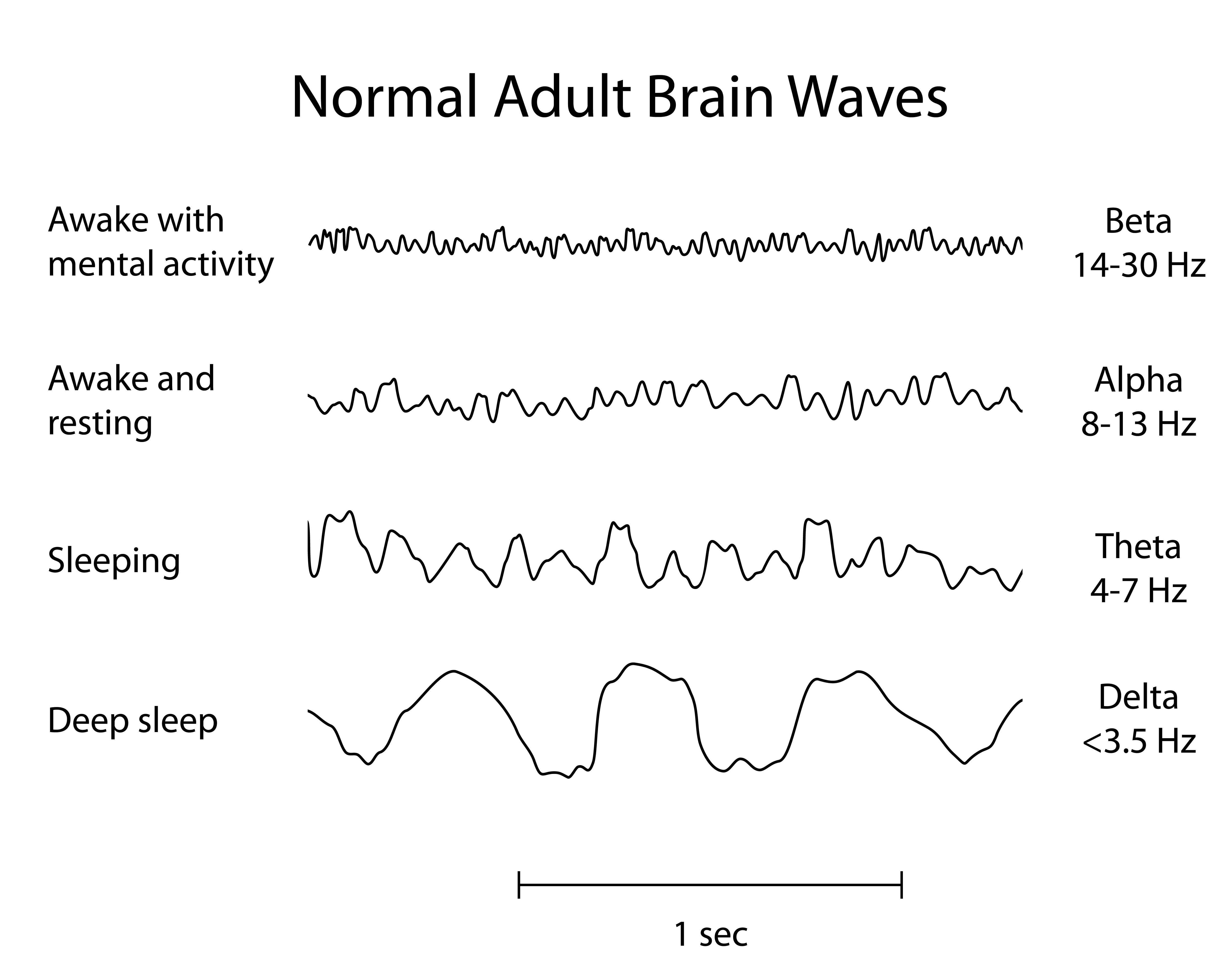
Studies have shown that poor quality sleep has a direct effect on cortisol levels, with one group of subjects experiencing a 37% increase in the hormone when they had only slept for 4 hours, and another study showing a 50% to 80% increase in cortisol among pilots who spent a week sleeping for 6 or fewer hours per night instead of their usual 7.8 hours. Slow wave sleep also suppresses the production of cortisol, which is known as “the stress hormone”-and for good reason, as it can cause anxiety, digestive problems, and even muscle breakdown. And while, ironically, it isn’t actually the deepest sleep possible, there are a lot of benefits that are unique to slow-wave sleep.įirstly, SWS is when the body produces the most prolactin, a hormone that boosts the immune system and manages inflammation. Once upon a time divided into stages 3 and 4, NREM 3 is what we call slow-wave sleep (SWS) and also goes by the names of deep sleep and delta sleep. Second are “spindles,” short bursts of high frequency brain activity. This element of NREM2 helps to not only integrate important information into the brain’s memory centers, but also retain learned muscle movements-something of particular importance to athletes. The first is called K-Complexes, which are variations in brain waves that help the mind ease into a deeper sleep by weakening the brain’s response to stimulus. Relieved of processing any external happenings, your neurons are able to “reboot,” consolidating the day’s memories and strengthening important lessons. This stands for “non rapid eye movement sleep, stage 2,” and comes right after the first phase of sleep, which is the lightest (so light, in fact, that people aroused from this stage often think they were completely awake). NREM 2 is usually a relatively shallow, dreamless sleep that lasts around 20 minutes, but it’s important because of two funky effects: And if you’re awoken during the night by, say, a thunderstorm, how tired you are the next day depends in large part on when you were woken up.Ĭonfused? Don’t be: While sleep is an unbelievably complex science, and a night of sleep comprises multiple distinct stages, there are really just three that you need to know about: NREM STAGE 2 What happens to you when sleep? Despite the fact that we spend a good third of our lives snoozing, most of us aren’t remotely aware of the fact that at different times of the night, we’re experiencing different stages of sleep.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
